Located 50 kilometres from Hindustan or the Republic of India, the island country of Sri Lanka has never suffered from a lack of attention from the world’s leading players. This is due to the island’s critical strategic position in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). Such a position always and for all such countries contains both positive and also potentially dangerous aspects.
It all depends on the state of affairs in the system of relations between the main players at a given moment in history. If the said players are not too suspicious of each other, quite a lot of benefits can be derived from the interest of each in influencing countries of Sri Lanka’s calibre. If the contradictions between the main players take a particularly acute form, it is possible for the smaller country, as they say, to ‘get heavy beating.’ Most likely, from both sides. This is not ‘out of spite,’ but simply because the ‘strategic environment’ may require so. Something similar happened to Sri Lanka during World War II.
 Former US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo with President Gotabaya Rajapaksa |
However, it was then a colony of the British Empire called ‘Ceylon.’ The Imperial Japanese Navy Command decided in the spring of 1942 to destroy the British Eastern Fleet based in the main port of Ceylon, Colombo. British Commanders became aware of this and began withdrawing ships to other bases. But Japan’s aircraft carrier forces still took a heavy toll, both on the British and (‘in passing’) on the port and inhabitants of Colombo. They also attacked the Trincomalee Port.
Nothing as bad is threatening the present Sri Lanka yet. On the contrary, there is a peak of ‘attention’ to the country by the major players, which today include China, India and the United States (US). Japan, for example, is increasingly asserting its presence in the IOR.
It is fundamentally important to note that in the struggle for influence over the so-called ‘Third World countries’ (i.e. the vast majority of humanity) the economic component of the ‘National Power’ available to the main players is increasingly effective. This is most clearly demonstrated by the new world power represented by the People’s Republic of China (PRC).
Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
The global Beijing Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) project already involves, in varying degrees, some 150 countries. Accustomed to swinging a military club (or, for the Japanese, a Katana) in the said struggle, the former Western colonisers suddenly discovered that it was much more productive to follow the cowboy principle: ‘Why steal a pretty girl - she could just be persuaded’ It should be added that, more often than not, Beijing does not have to bother itself much with persuasion, because the differently coloured ‘pretty girls’ (of Asia, Africa, Latin America) are ready to accept much needed assistance in the development of transport and industrial infrastructure, agricultural facilities, education and healthcare, in the fight against chronic epidemics.
The process is not without its costs (‘debt traps’ sometimes arise), but so far nothing particularly dangerous for Beijing’s partners has arisen. Rumours of Uganda losing control of the only international airport at Entebbe, near Lake Victoria, have not been confirmed. The new world power is engaged in far bigger games to have its image spoiled by all sorts of ‘trivialities.’
Too late to realise the real cause and source of threats to positions in the former colonies, the former metropolises rushed to compose their versions of the BRI, ‘but better.’ On December 1, 2021, the European Commission (EC), i.e. the de facto European Union (EU) Government, announced the launch of its own project called the Global Gateway, through which smart, transparent and secure connections with the outside world will be organised. This was a kind of European contribution to the global project of a generalised West, Build Back Better World, announced in June 2021 during a regular G7 Summit in Cornwall, in the United Kingdom (UK).
Exclusively for the Indo-Pacific region, where the focus of the current stage of the ‘Great Game’ is shifting, and consequently key US foreign policy interests, US President Joe Biden initiated the so-called ‘Economic Strategy Framework’ at the end of October 2021 (the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework).
In general, the generalised West has produced many words and beautiful acronyms in the direction of the ‘Third World’ in recent months. So far, however, they have not led to any concrete results - results similar to what Beijing can demonstrate, including in Sri Lanka. Because today the strategic importance of this country is determined by the fact that it is located on one of the world’s most important trade routes, acting as an intermediate hub on it. It is as important as Singapore.
But in order to fulfill this role properly, the available port facilities need to be state-of-the-art. And the upgrading of the same Port of Colombo is being carried out by Chinese companies. Moreover, a new hub, Hambantota, is being built on the Southern tip of the island, which was previously completely deserted. Western propaganda links the fact that Chinese companies received an order to build this port to offset Sri Lanka’s financial debts to the PRC.
 These do exist, but they are not clearly linked to the fact that Beijing was given the right to build Hambantota and the subsequent 99-year lease on the Port. Moreover, an undertaking has been obtained from China not to use Hambantota for military purposes. Beijing says it does not need to, as the Pakistani Port of Gwadar on the Arabian Sea, which incidentally is the terminus of Pakistan’s (one of the most important) BRI land route, is sufficient for such purposes. The same role will not be ruled out for Hambantota as a crucial transshipment point for the BRI maritime portion.
These do exist, but they are not clearly linked to the fact that Beijing was given the right to build Hambantota and the subsequent 99-year lease on the Port. Moreover, an undertaking has been obtained from China not to use Hambantota for military purposes. Beijing says it does not need to, as the Pakistani Port of Gwadar on the Arabian Sea, which incidentally is the terminus of Pakistan’s (one of the most important) BRI land route, is sufficient for such purposes. The same role will not be ruled out for Hambantota as a crucial transshipment point for the BRI maritime portion.
Quad Alliance
Again, it is not surprising that the main geopolitical opponents of the PRC, above all the US, are paying close attention to Sri Lanka. In particular, the country was one of the points of visit for Mike Pompeo during his last (late 2020) trip abroad as the US Secretary of State. Negotiations with the leadership of Sri Lanka and several other countries visited (above all Vietnam) have been exploratory as to the possibility of expanding the newly formed Quad Alliance configuration comprising the US, Japan, India and Australia. In Colombo, Pompeo made a number of amusing remarks, stating in particular the ‘partnership’ nature of the US coming to a country, as opposed to the ‘predatory’ policies of the PRC in the same countries.
But the main destination of Pompeo’s said tour was India, which is also the main opponent of China’s in the struggle for influence in Sri Lanka. It was the problems in Chinese-Indian relations that once again came to light during the struggle to win the order for the construction of the Hambantota Port.
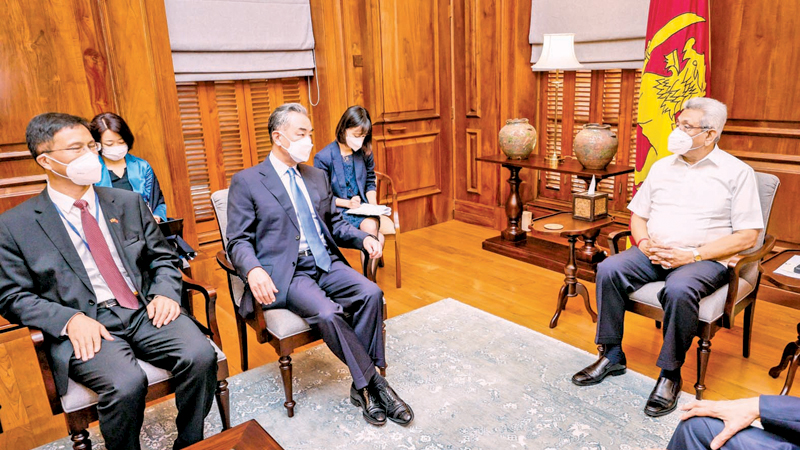
Unfortunately, the competition between the two Asian giants for influence in Sri Lanka and other crucial island states in the Indian Ocean (Maldives, Mauritius, Seychelles) has not abated since then. The visit of Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi to Sri Lanka in early January this year during his traditional annual tour of a number of countries in Africa and the Indian Ocean Island States (IOIS) was met with suspicion in New Delhi.
It is important to bear in mind the complexity of the situation in which the latter find themselves, as they have to manoeuvre in the field of tensions that are being shaped in the region by the world’s leading players. Each of them has its own interests to uphold. The main purpose of the visit to India in early February this year by Foreign Minister Prof. Gamini Lakshman Peiris seems to have been to reassure New Delhi that the bilateral relationship was not threatened.
In a demonstration that India is always ready to help its Southern neighbour in an emergency, India concluded an agreement in mid-February to supply Sri Lanka with 40,000 Cubic Metres of diesel and petrol, which proved to be an extremely timely step in the context of the growing energy crisis in the island.
However, once again, the situation around Sri Lanka is an important indication that the state of China-India relations is becoming one of the major factors shaping developments not only in the Indian Ocean Region, but also in the entire Indo-Pacific Region.
(Vladimir Terekhov is an expert on the issues of the Asia-Pacific region)

Hambantota Port
- New Eastern Outlook


Add new comment